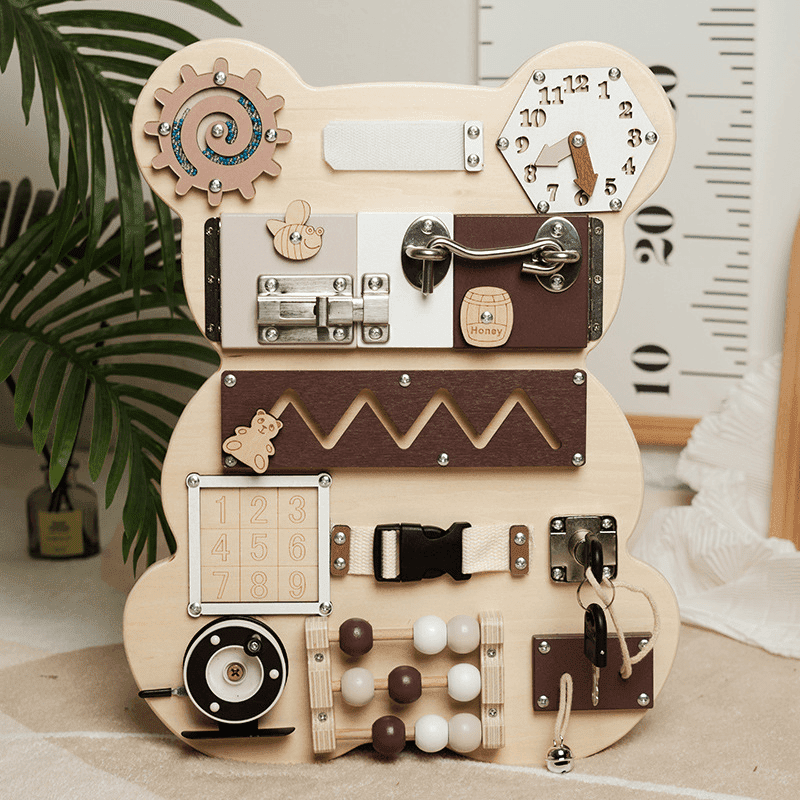
How to develop fine motor skills?
Writing a birthday card or tying your shoelaces certainly seem like very simple tasks to most people. However, these hobbies really involve intricate motions that call for brain and muscular coordination.
The capacity to move by using the little muscles in the hands and wrists is known as fine motor abilities. These abilities need the ability to synchronize your hands, fingers, and eyes.
We employ fine motor skills in a range of daily activities, thus developing these abilities is an extremely crucial component of our development.
What distinguishes vast motor abilities from fine motor abilities?
Gross motor skills refer to the coordination of the bigger muscles in the arms or legs with the eyes, as opposed to fine motor skills, which include the muscles in our hands or wrists.
Therefore, gross motor skills are necessary for bigger motions like walking or tossing a ball, but fine motor skills are necessary for tiny movements and activities like picking items up or holding a pencil.
Several tasks call on the usage of our fine motor skills, such as:
- A pen, pencil, or paintbrush in their hand
- Neatly tracing, sketching, and writing
- Arranging and stacking items
- Using rulers and scissors
- It might be challenging at first to fasten garments with zips, buttons, and velcro.
- Opening lunch boxes: Food containers' closures might be screw caps or clips.
- Shoelace tying
- Video game controllers feature tiny buttons and call for quick responses.
- Fork and knife use: If you don't hold them properly, food may not remain on the utensil or the youngster may take a very long time to finish their meal.
- Using toothpaste.
- Playing an instrument is an illustration of a fine motor ability that some individuals try to perfect throughout their lives but occasionally never accomplish. It frequently involves minute, deft finger motions that must be timed and placed precisely. Because of this, parents and educators frequently advise kids to start taking music lessons at an early age. Even if they never become professional musicians, their dexterity (the capacity to move their hands rapidly and purposefully) will significantly increase.
Improved Fine Motor Skills:
Although each child develops fine motor skills at a different rate, most fine motor skills development typically takes place between the ages of 6 and 12. Children will develop their fine motor abilities in various ways depending on their developmental stage.
Each child's fine motor skills development progresses differently, and it depends on the age-appropriate growth of a few physical abilities that can serve as a foundation for arm and hand control.
The following list of achievements can be anticipated at various ages:
1. Babies:
- Reflexes play a major role in the development of fine motor skills when we are infants.
- The "palmar hold," in which infants cling onto a person's finger by wrapping their hand around it, is a nice illustration of this.
- Before being 12 months old, newborns could learn to exchange toys between their hands and pick up things with a pincer hold (using their thumb and one finger).
- Babies may not reach these milestones for a variety of reasons, including inadequate muscular control and growth.
- Some recommedation toys for your babies: montessori wooden object permanence box, wooden rattles, spinning drum, etc.

2. Toddlers:
Children learn via play at this period of fine motor skill development. Understanding that various items have varied weights and sizes is a crucial ability that infants acquire.
Toddlers will engage with the following toys and games that can aid in the development of fine motor skills:
- Using bricks to construct towers
- Drawing using crayons, colored pencils, and pens
- Affixing beads and buttons to ribbon and string
- Play-Doh play, particularly forming little balls or sausage forms
- Paging through image books

3. Pre-school:
Children will have mastered some fundamental fine motor abilities by this age, enabling them to grasp a pencil, cut and stick, and construct objects out of blocks.
Children may construct more complicated forms than toddlers by manipulating materials like clay or dough, which is another way they can enhance their fine motor skills.
At this age, kids could learn how to sustain things like paper when playing and sketching by using their non-dominant hand.
Other exercises that will improve the fine motor abilities of preschoolers include:
- Cutting a continuous line with scissors while writing their name and the digits 1–5.
- Using zippers and buttons separately
- At this age, a poor pencil grip or irritation with pencil holding might hinder growth.
4. Primary School:
Children in elementary school will be required to execute tasks that require the Use of fine motor skills, such as:
- Using shapes to cut
- Following the guidelines
- Accurately from the letters and numbers.
- Don't stray from the lines.
- Their shoelaces are tied individually.
- Ideas for fine motor skill development at home
- Encouraging children to play with small toys and playdough
- Completing puzzles
- Threading beads onto pipe cleaners
It has been shown that a child's capacity from birth to a certain age is crucial to their total physical and mental development. Please pay great attention to these abilities as parents! particularly with fine motor skills. I sincerely hope that sharing is helpful to the readers. Stay tuned for the next subject!